Last updated on January 11th, 2025 at 11:09 am

There are different types of wired and wireless transmission media. These are used to set up the different types of networks that exist today. Let’s embark on a journey to learn about what transmission media are, the types of transmission media, and how they have revolutionized the way we interact and exchange data in the modern world. In this article, the topics covered are:
- What a transmission media is;
- Types of wireless transmission media;
- Types of wired transmission media; and
- What are twisted pair, coaxial, and fiber optic cables.
Transmission media are used to set up intranets, extranets, and the internet. These have changed over time, and wireless network technologies have changed the way we connect computing devices.
What is transmission media?
A transmission media is a communication channel used to transmit information from the source to the receiver. It is also known as a physical path for data transfer through electromagnetic signals.
Wireless transmission media
Wireless transmission media, as the name suggests, refers to the technology used to transmit information from one device to another without the use of a physical connection.
The types of wireless transmission media are Bluetooth, cellular radio, broadcast radio, microwave, communication satellite, sensors, and infrared.
Have you ever wondered about how far the cell phone has come since it was first introduced? Explore mobile networks to learn more.
Wired transmission media
Unlike wireless transmission media, wired transmission media refers to the use of a physical path to connect two or more devices.
The types of wired transmission media are coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, ethernet, fiber optics cable, stripline, and microstrip line.
What is a twisted pair cable?
A twisted pair cable is a type of cable where two communication lines are twisted together to improve electromagnetic compatibility. It is this design, two wires twisted together, that gives this transmission media its name. These cables are located in a plastic insulator and come in pairs of four or more communication lines that are twisted and packed together to create a network cable.
There are two types of twisted pair cables. These are:
- Shielded and;
- Unshielded twisted pair cables.
For further reference, see the diagram here:
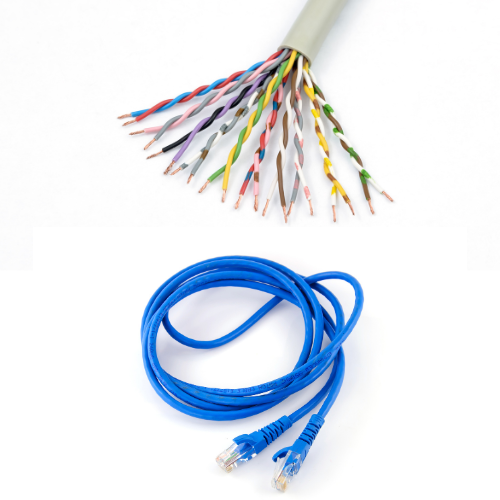

What is a twisted pair cable used for?
Twisted pair cables are mostly used in networking and communication, for example, telephone lines, digital lines, and local area networks.
What is a coaxial cable?
A coaxial cable is a type of network cable that is made up of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield with the two separated by a dielectric. Most coaxial cables come with an outer layer of protection.
What does a coaxial cable look like?
Here’s what a coaxial cable looks like:
- Inner Conductor: At the coaxial cable’s center is a solid strand of wire, typically made of copper or aluminum.
- Insulation: Surrounding the inner conductor is a layer of insulating material, usually made of plastic.
- Metallic Shield: There is a metallic shield over the insulating layer, which is often made of aluminum or a combination of aluminum and foil.
- Outer Insulation: The outer layer of the coaxial cable is another layer of insulation, providing additional protection from the environment;
- Connectors: Coaxial cables have connectors on each end to connect to devices or to interface with other cables or equipment. Common connectors for coaxial cables include F-type connectors, BNC connectors, and N-type connectors, among others.
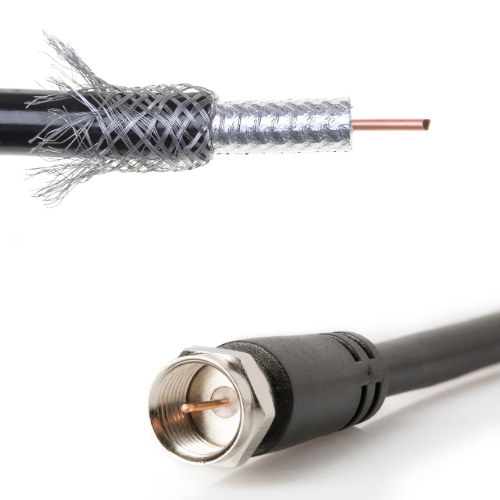

What is a coaxial cable used for?
Coaxial cables are used for cable television systems, internet connections (e.g., cable internet), and for connecting antennas to televisions and other devices. They come in various sizes and specifications, with differences in terms of signal quality, bandwidth, and applications. The specific appearance of a coaxial cable may vary depending on its type and intended use, but the layered construction described above is common to most coaxial cables.
What is a fiber optic cable?
A fiber optics cable is a cable that is made up of thin strands of glass that is used to send data from one PC to another at light speed. Fiber optic cables are able to send information at a much higher bandwidth than the twisted pair cable. More importantly, they are better for transmitting data over long distances.
What does a fiber optic cable look like?
Fiber optic cables vary from manufacturer to manufacturer and based on their intended use. However, the core components, including the transparent fiber strands and the outer jacket, are common features of most fiber optic cables. Below are the basic components of the fiber optic cable:
- Fiber Strands: The core component of a fiber optic cable is one or more hair-thin strands of glass or plastic fibers.
- Color: the most common colors for the fiber cable outer jacket are yellow, orange, aqua for multimode fibers, or blue for single-mode fibers;
- Outer Jacket: The outer jacket provides protection to the inner components from environmental factors, physical damage, and UV radiation. The color of the outer jacket can vary depending on the cable’s intended use;
- Connectors: Fiber optic cables often have connectors on one or both ends. These connectors allow the cable to be easily connected to network devices, such as switches, routers, transceivers, and optical modules. The connectors are typically made of plastic or metal and have specific shapes and sizes for compatibility with different types of ports;
- Flexibility: Fiber optic cables are very flexible and can be bent or twisted without significantly affecting their performance;
- Labels and Markings: Fiber optic cables often have labels or markings along their length to provide information about the cable type, manufacturer, and other relevant details. These markings help with cable identification and maintenance.
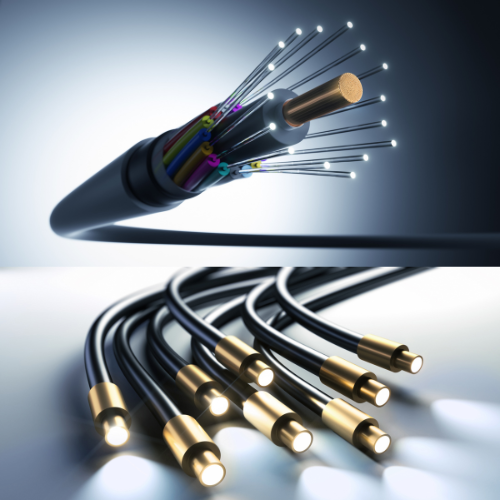
Fiber optic cable
Transmission media require the use of other devices to make connectivity and communication work well. To make network communication possible, switches, modems, routers, and network adapters are also a necessary part of many computer networks.
What is a fiber optic cable used for?
Fiber optic cables are used for transmitting data, typically in the form of light signals, over long distances with high bandwidth and minimal signal loss. They have a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
- Telecommunications
- Internet Connectivity
- Cable Television
- Data Center
- Medical Imaging
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Undersea Cables
- Industrial Automation
- Security Systems
- Sensor Networks
- Research and Scientific Applications
Overall, fiber optic cables are favored for their high data transmission rates, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and their ability to transmit signals over long distances, making them indispensable in modern communication and technology infrastructure.
Before you go
We try our best to be as thorough as possible in the information we provide. However, if you have any questions or comments about wired and wireless transmission media, be sure to leave them in the section provided below, and we will get back to you in a timely manner.
 Skip to content
Skip to content