Last updated on June 22nd, 2024 at 12:59 pm

Network topology is a term used to refer to the network architecture. It refers to the manner in which nodes (computers, modems, switches, printers, etc) and links (wires) are arranged in a network. There are different types of network topologies. The type used may be influenced by your budget, need for speed, space, and more. Keep reading to learn:
- The types of network topologies and
- Advantages and disadvantages of each type.
What are the types of network topologies?
The types of network topologies are:
- Bus topology;
- Ring topology;
- Star topology;
- Mesh topology and
- Tree topology.
Network topologies are not the same as types of networks, and they do not influence network privacy as much as your use of intranet, internet, or internet does.
Bus topology
A bus or line topology is a network in which all devices, including printers, computers, and scanners, are connected to a single communication line or backbone.
This single cable makes it possible for devices to share resources and communicate with each other.
Advantages of bus topologies
Some advantages of using the bus topology are:
- Cost-effective: This type of topology would require less investment than other topologies to set up;
- It requires less cable to set up than the star, mesh, or tree topology;
- Simplicity: Bus topology is easy to set up and connects devices, providing a simple and flexible network setup; and
- Easy extensions: This type of topology is easily extended, making limited extension straightforward.
Related article: Mobile networks in education
Disadvantages of bus topologies
Some disadvantages of using the bus topology are:
- Limited bandwidth: The channel used for communication may have limited bandwidth, thus affecting the data transmission speed;
- If the cable is damaged, the network splits into two, causing all nodes beyond that point to go down;
- Not suitable for a large network;
- Speed: As more devices are added, the network slows down;
- Single point of failure: If there is an issue with the central bus, the entire system will have an issue until the problem with the central bus is fixed; and
- Collision issues: There may be feedback when multiple devices try to send out data all at once.
Ring topology
This type of topology has all the devices connected in a singular loop, going in a circular style. Each node in the ring network connects to two others, which in turn forms a continuous path.
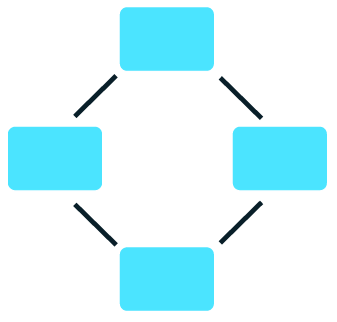
Advantages of ring topologies
The advantages of ring topology are:
- High data transmission rate: This ensures that data transmission is efficient when communicating using the network;
- Easy problem identification: With this feature activated, we can ensure that locating and solving problems will be easy and efficient; and
- Minimal impact of device failure: This feature ensures that other devices would not be affected if one of the devices experiences any type of technological difficulty.
Disadvantages of ring topologies
Some disadvantages of the ring topology are:
- Slower speed compared to some of the alternatives: Although more effective than the bus, this topology is less efficient than the others in the long run.
- Data passes through each workstation: This poses a threat to all the computers that are connected to the network due to the risk of spreading potential viruses.
Star topology
A star topology is a network topology in which each device (such as computers, printers, or other peripherals) is connected directly to a central hub or switch.
In a star topology, the central hub acts as a distribution point, facilitating all communication between devices in the network.
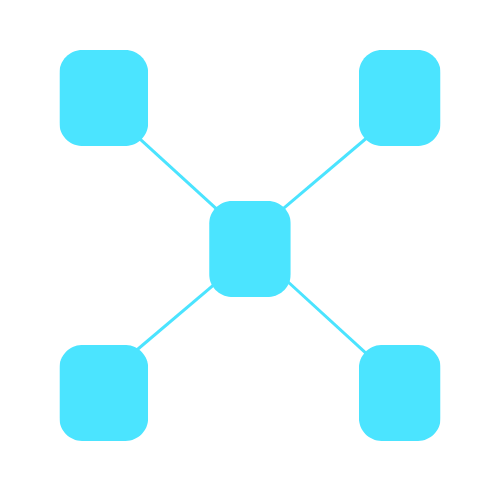
Advantages
Some advantages and disadvantages are:
- Scalability: This type of network is very flexible and expandable when it comes to adding more devices.
- Easy to install: The set-up process is relatively simple and easy to complete.
- Durable: This type of setup can run smoothly even if one of the connections fails.
Disadvantages
- High cost: The cost of setting up the central hub is relatively high, and damage to it can disrupt the entire network.
- Dependency on the central device: The network functionality is heavily dependent on the central hub; if that fails, the entire network will malfunction.
Mesh topology
A mesh topology has all the devices connected to each other, creating a redundant network. In a mesh topology, the connections between devices are typically point-to-point, creating a redundant and robust network infrastructure.
Some advantages and disadvantages of mesh topology are:
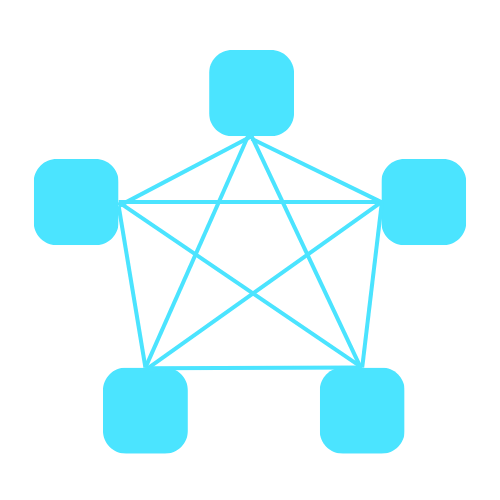
Advantages
Some advantages of mesh topology are:
- Redundancy: Mesh topology is good at dealing with failures while also ensuring the smooth operations and reliability of the network.
- High data handling capacity: The mesh topology can handle large amounts of data while ensuring a fast and efficient data transfer process.
- Scalability: This shows the flexibility of mesh topology while also allowing for the handling of multiple devices connecting to the network.
Disadvantages
THe following are a list of disadvantages of the mesh topology:
- Cost of implementation: Mesh topology is more costly when compared to a network such as a bus or star;
- Complexity: The advanced level of interconnection can often lead to issues with setup and maintenance.
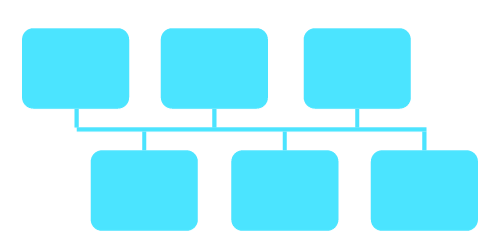
Tree topology
This type of topology combines the star and bus topologies, forming a new social order. some advantages and disadvantages of tree topology are:
Advantages:
Some advantages of the tree topology are:
- Scalability: Easily changed to suit the amount of data currently on the network by adding branches or nodes.
- Centralized control: The root node offers centralized management.
- Reliability: Redundancy in the path enhances network reliability.
Disadvantages
There are a few cons associated with the tree topology. These are:
- Dependency on root nodes: Root nodes are the core of the tree topology. If that is damaged, the entire system may experience various serious issues.
- Complexity: Because it is a tree topology, it is expected to be a little complicated to operate and maintain.
Networks use different types of transmission media to aid connectivity. Explore wireless transmission media to learn more.
Hybrid topology
Hybrid topology combines two or more topologies. While it shares similarities with the tree topology, it offers a wider range of merging topologies. Some advantages and disadvantages of a hybrid topology are:
Advantages:
- Flexibility and efficiency: The hybrid topology is highly flexible, which also makes it efficient. This flexibility means that a hybrid approach allows for the integration of various components, adaptability to different requirements, or the ability to combine the strengths of different technologies.
- Reliability: It is a very safe and reliable network structure. If one node has an issue, it won’t prevent the others from working.
- Customization: You can customize hybrid topology by combining different topologies to meet specific network requirements.
Disadvantages:
- Complex design: Hybrid topology designs are more complex than other topologies, making them harder to maintain and set up.
- Costly: Given the complex and intricate design of this specific topology, it is very expensive to set up.
- Potential performance issues: If the core of the hybrid topology is damaged, it will cause performance issues throughout the network, hence the need for a robust infrastructure.
 Skip to content
Skip to content