Last updated on January 18th, 2026 at 01:36 pm

Like other programming languages, loops in Python are a powerful way to condense code blocks and make them more dynamic. They make it easy for our codes to adapt based on user input.
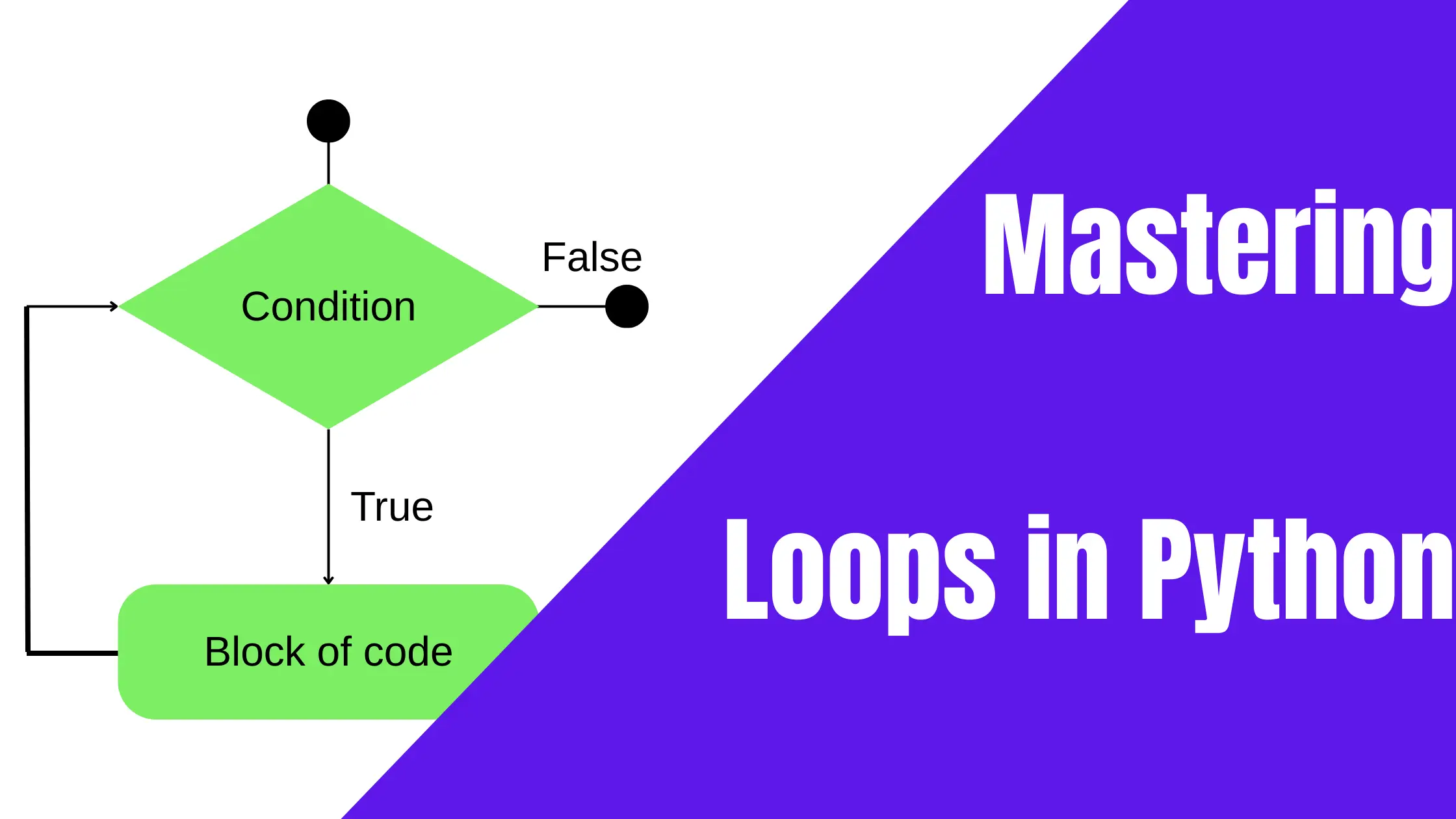
Loops allow a program to repeatedly iterate a block of code. As such, they are used for repetitive structures. It is crucial to properly comprehend the programming syntax in order to use the language effectively.
In this lesson, we will explore:
- What are loops in Python;
- Types of loops;
- How to write for loops in Python;
- How to use a while loop; and
- What are nested loops in Python.
Types of loops in Python
Python provides two primary types of loops. In this lesson, we will delve briefly into these two types of loops and their applications.
One of the loops used in Python is the for loop. This type of loop is used to go over a sequence. Some examples of such sequences are: tuples, strings, ranges, or lists. or iterable objects, executing a block of code.
The for loop
In Python, for loops enable us to iterate through a sequence of items.
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry"]
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)This loop has an output that looks like this:
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
The other loop provided is a while loop, this type of loop repeatedly executes a line of code according to the specified condition.
The while loop
In Python, as with most programming languages, the while loop uses a condition to control the execution of a program. As long as the condition is true, the program will continue to run.
As with conditionals, the indentation marks the areas that are controlled by the loop. If the indentation is not done correctly, the program will not work as expected.
Here is an example of a while loop.
count = 0
while count < 9:
print(count)
count += 1In the above example, line 2 (count<9) holds the condition that governs the iteration. The last two lines will be executed as long as the condition is true.
Here is what the output looks like:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
As you can see, all of the numbers printed are less than 9.
Nested loops in Python
Have you ever heard the term nested loops? In programming languages nested loop is a term used to refer to a loop within another loop.
This specific type of loop is useful when we wish to perform iterations over multiple sequences of data. Here is a simple example of a nested loop.
Let’s combine the above loops to see what happens. Here, I have added 2 modifications. Count is now equal to 1, and the condition is count <=9.
count = 1
while count <= 9:
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry"]
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
print(count)
count += 1The loop above will repeat 9 times. Here is the output:
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
1
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
2
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
3
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
4
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
5
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
6
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
7
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
8
apple
banana
cherry
date
elderberry
9
Control statements in Python loops
The final part of loops is control statements. There are three control statements used in loops: else, break, and continue.
Else: Else can be included in both for and while loops; it will only execute if the loop continues without encountering a break statement
Break: This statement terminates the loop entirely, exiting the loop block and continuing execution after the loop is completed.
Continue: This will be used to skip the current iteration of the loop and proceed to the next iteration.
To learn more about control structures in Python, be sure to visit Loop Iteration in Python.
What are the three types of loops in Python?
Python only has two types of loops: while and for loops. The other type of loop often talked about is a nested loop. However, nested loops are simply loops within loops, but they still utilize the while and for loops.
Why do we use while loops in Python?
We use while loops to control repetition that uses a condition. Let’s look at an example:
count = 1
while count <= 2:
print(count)
count += 1
Think of the variable called ‘count‘ in the program above. At the beginning of the program count held 1. Line 2 sets the condition for the count to be no more than 2.
The next line prints the value count holds, while the last line is used to increase the value in count by 1. Once the count becomes higher than 2, the program exits.
How do you loop from 1 to 5 in Python?
In Python, there are several ways to loop from 1 to 5 in Python. Here is an example:
count = 0
while count < 5:
count+=1
print(count)
That’s it. This is a simple program that loops from 1 to 5. For clarity, we added a line that prints the content of the variable count.
 Skip to content
Skip to content